Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS
Discover the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS! Learn how to perform, understand SPSS output, and report results in APA style. Check out this simple, easy-to-follow guide below for a quick read!
Struggling with the Wilcoxon Rank Test in SPSS? We’re here to help. We offer comprehensive assistance to students, covering assignments, dissertations, research, and more. Request Quote Now!
1. Introduction
The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS offers a robust method for analysing paired data, especially when assumptions of normality are questionable. This non-parametric test provides an alternative to the paired sample t-test, allowing researchers to compare two related samples or repeated measurements on a single sample. The test ranks the differences between pairs of observations, considering the direction and magnitude of these differences.
In this blog post, we will explore the various facets of the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS, from its foundational principles to practical implementation and interpretation. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this statistical tool, its applications, and how to report your findings following APA guidelines.
2. What is the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in Statistics?
The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test is a non-parametric statistical test used to compare two related samples. Unlike the paired sample t-test, it does not assume a normal distribution of the differences between pairs. Instead, it evaluates the differences between pairs of observations, ranking these differences by their absolute values while maintaining their sign.
Developed by Frank Wilcoxon in 1945, this test serves as a robust alternative when data do not meet parametric assumptions. It is particularly useful for small sample sizes or when dealing with ordinal data. The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test evaluates whether the median difference between pairs is significantly different from zero, offering insights into changes or differences between conditions or time points.
3. What is the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test used for?
Researchers use the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test primarily to assess differences between paired observations. It is ideal for situations where the same subjects undergo two conditions, such as before-and-after studies, or when measurements are taken at different times. This test is also valuable in clinical trials and psychological studies where the normality assumption is often violated.
For instance, in medical research, the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test can compare the effectiveness of a treatment by evaluating pre-treatment and post-treatment measurements. Similarly, in psychology, it might assess the impact of an intervention on participants’ scores before and after the treatment. The test’s versatility makes it a preferred choice for various fields requiring paired data analysis.
4. What is the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS?
In SPSS, the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test provides a user-friendly way to perform non-parametric comparisons between paired samples. The software simplifies the process, offering clear steps to input data, run the test, and interpret the results. Researchers can easily navigate through the menu options to apply this test to their data sets.
SPSS handles the computation and ranking of differences, producing output tables that display the test statistics and significance levels. This functionality enables researchers to focus more on interpreting the results rather than the complexities of manual calculations. Using SPSS for the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test ensures accuracy and efficiency in statistical analysis.
5. What is the difference between the Paired Sample t-test and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test?
The paired sample t-test and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test both compare two related samples, but they differ in their assumptions and application. The paired sample t-test assumes normally distributed differences between pairs, making it suitable for interval or ratio data. In contrast, the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test does not require normality, making it appropriate for ordinal data or non-normally distributed interval data.

Additionally, the paired sample t-test evaluates the mean difference between pairs, while the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test assesses the median difference. This distinction makes the Wilcoxon test more robust against outliers and skewed distributions. Researchers often choose the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test when the data do not meet the parametric assumptions required for the paired sample t-test.
6. What Are Other Nonparametric Tests?
- Mann-Whitney U Test: Compares differences between two independent groups when the data are not normally distributed.
- Kruskal-Wallis Test: Extends the Mann-Whitney U Test to more than two groups, assessing rank differences—nonparametric alternative to One-Way ANOVA Test.
- McNemar Test: Used for paired nominal data to determine changes in proportions.
- Friedman Test: Nonparametric alternative to repeated measures ANOVA, comparing ranks across multiple related groups.
- Sign Test: Evaluates the median of a single sample or compares medians of two related samples.
- Cochran’s Q Test: Extension of the McNemar test for more than two related groups.
- Kendall’s W: Assesses the agreement between raters.
- Binomial Test: Tests the observed proportion against a theoretical proportion.
- Jonckheere-Terpstra Test: Tests for ordered differences among groups.
- Wald-Wolfowitz Runs Test: Evaluates the randomness of a sequence.
- Marginal Homogeneity Test: Assesses changes in proportions in paired categorical data.
- Median Test: Compares the medians of two or more groups.
7. What are the Assumptions of the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS?
- Paired Observations: Each data point in one sample must have a corresponding data point in the other sample.
- Ordinal or Continuous Data: The test requires ordinal or continuous data.
- Symmetry: The distribution of the differences between pairs should be symmetric.
- Independence: Observations should be independent of each other.
Meeting these assumptions ensures the validity of the test results. Violation of these assumptions can lead to inaccurate conclusions, making it crucial to verify them before proceeding with the analysis.
8. What is the Hypothesis of the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS?
In the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test, the hypotheses focus on the median difference between paired observations.
- The null hypothesis (H0): the median difference between pairs is zero.
- The alternative hypothesis (H1): the median difference between pairs is not zero.
Testing these hypotheses helps determine whether the observed changes are statistically significant, guiding researchers in drawing meaningful conclusions from their data.
9. An Example of the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS
Consider a study assessing the impact of a new teaching method on students’ test scores. Researchers collect scores before and after implementing the method. To analyse the data, they input the scores into SPSS, ensuring each student’s pre-test and post-test scores are paired correctly.
Running the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS, researchers find the ranks of the differences between pre-test and post-test scores. The output reveals whether the new teaching method significantly affects student performance. This example illustrates the test’s practical application, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of educational interventions.
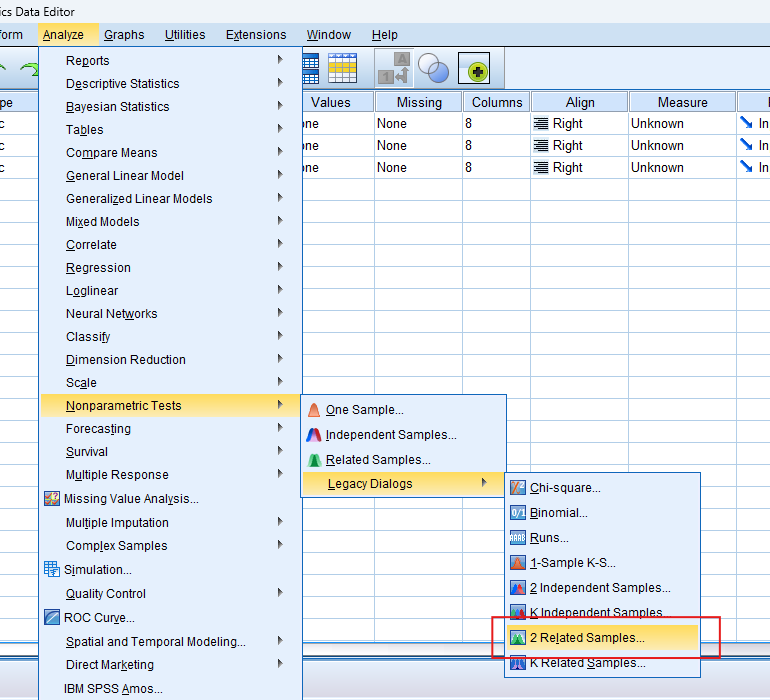
Step by Step: Running the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS Statistics
Let’s embark on a step-by-step guide on performing the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test using SPSS
- Input Data: Enter the data into SPSS, ensuring that the dependent variable (e.g., test scores) and the independent variable (e.g., group type) are correctly labelled.
- Select the Test: Navigate to ‘Analyze’ > ‘Nonparametric Tests’ > ‘Legacy Dialogs’ > ‘Related Samples’.
- Choose Variables: Select the two variables representing your paired data
- Run Test: Click `OK` to run the test
- Review Output: SPSS will generate output tables with the test statistics and p-value.
Note: Conducting the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test in SPSS provides a robust foundation for understanding the key features of your data. Always ensure that you consult the documentation corresponding to your SPSS version, as steps might slightly differ based on the software version in use. This guide is tailored for SPSS version 25, and for any variations, it’s recommended to refer to the software’s documentation for accurate and updated instructions.
11. SPSS Output for Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
12. How to Interpret SPSS Output of the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
Upon running the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in SPSS, you will receive output tables that display key statistics.
- The `Test Statistics` table includes the Z-value and the asymptotic significance (p-value). A p-value less than 0.05 typically indicates a significant difference between the paired samples.
- The `Ranks` table shows the number of positive, negative, and tied ranks. Positive ranks indicate instances where the second measurement exceeds the first, while negative ranks show the opposite. Tied ranks represent equal measurements.
Interpreting these tables helps determine the direction and significance of the differences observed.
13. How to Report Results of the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in APA
Reporting the results of Wilcoxon signed rank test in APA (American Psychological Association) format requires a structured presentation. Here’s a step-by-step guide in list format:
- Introduction: Begin by describing the purpose of the analysis. The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test aims to determine whether there is a significant difference between paired observations, particularly when the data do not meet the assumptions required for parametric tests such as the paired sample t-test.
- Method: Detail the data collection process and the variables involved. Specify that the test ranks the absolute differences between paired observations, considering the direction of these differences.
- Results: Present the key statistics from the SPSS output. Report the Z score and the asymptotic significance (p-value).
- Discussion: Interpret the results, highlighting the significance of the findings. Explain what the lack of a significant difference means in the context of the research question.
- Conclusion: Summarise the main points of the analysis. Reinforce the finding that there was a significant difference between pre-test and post-test scores, implying the effectiveness of the new teaching method.

Get Help For Your SPSS Analysis
Embark on a seamless research journey with SPSSAnalysis.com, where our dedicated team provides expert data analysis assistance for students, academicians, and individuals. We ensure your research is elevated with precision. Explore our pages;
- SPSS Help by Subjects Area: Psychology, Sociology, Nursing, Education, Medical, Healthcare, Epidemiology, Marketing
- Dissertation Methodology Help
- Dissertation Data Analysis Help
- Dissertation Results Help
- Pay Someone to Do My Data Analysis
- Hire a Statistician for Dissertation
- Statistics Help for DNP Dissertation
- Pay Someone to Do My Dissertation Statistics
Connect with us at SPSSAnalysis.com to empower your research endeavors and achieve impactful data analysis results. Get a FREE Quote Today!